What is a car engine? Simply put, a car engine is a complex machine made up of many mechanisms and systems. So, what is the structure of the car engine? No matter which kind of car engine, to complete the energy conversion, to achieve the work cycle, to ensure long-term continuous normal work, must have two major institutions and five systems (car engine type). Let us first look at the two major mechanisms of the car engine: the crank linkage mechanism and the valve train. (Car engine working principle)
This article refers to the address: http://
(1) Crank and link mechanism
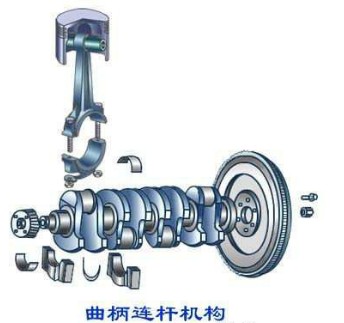
The crank-link mechanism is the main moving part of the engine to achieve the working cycle and complete the energy conversion. It consists of a body group, a piston rod set and a crankshaft flywheel set. During the power stroke, the piston is subjected to linear motion in the cylinder by the gas pressure, converted into a rotary motion of the crankshaft through the connecting rod, and externally outputs power from the crankshaft. In the intake, compression and exhaust strokes, the flywheel releases energy and converts the rotational motion of the crankshaft into a linear motion of the piston.
(2) Gas distribution mechanism
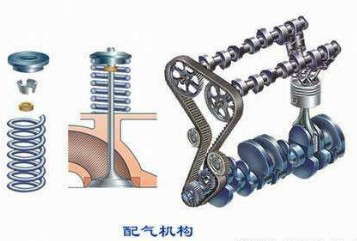
The function of the valve train is to open and close the intake and exhaust valves according to the working sequence and working process of the engine, so that the combustible mixture or air enters the cylinder and exhausts the exhaust gas from the cylinder to realize the ventilation process. Most of the gas distribution mechanisms adopt an overhead valve type gas distribution mechanism, which is generally composed of a valve group, a valve transmission group and a valve driving group.
After understanding the above two institutions, we will look at its five major systems: starting system, fuel supply system, cooling system, lubrication system, ignition system.
(1) Starting system
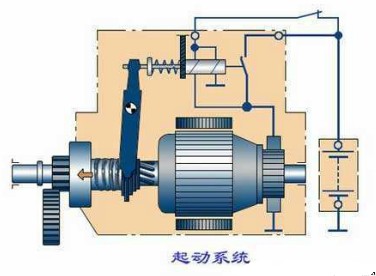
In order to make the engine transition from a static state to a working state, the crankshaft of the engine must first be rotated by an external force to reciprocate the piston, and the combustible mixture in the cylinder is burned and expanded to push the piston downward to move the crankshaft. The engine can run on its own and the work cycle can be automated. Therefore, the crankshaft starts to rotate under the action of an external force until the engine starts to automatically idle, which is called starting of the engine. The device required to complete the starting process is called the starting system of the engine.
(2) Fuel supply system
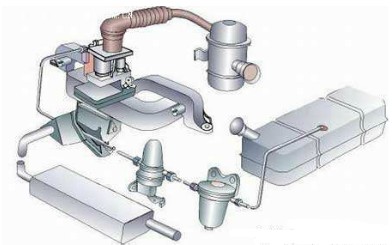
Fuel supply system
The function of the gasoline engine fuel supply system is to formulate a certain amount and concentration of mixed gas according to the requirements of the engine, supply it to the cylinder, and exhaust the burned exhaust gas from the cylinder to the atmosphere; the function of the diesel fuel supply system is to use diesel fuel. The air is supplied to the cylinder separately, a mixed gas is formed in the combustion chamber and burned, and finally, the burned exhaust gas is discharged.
(3) Cooling system
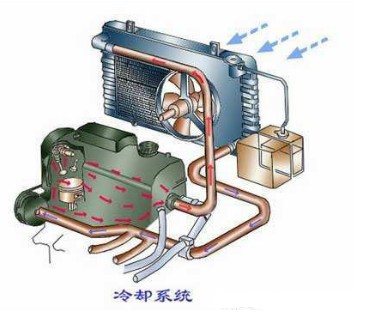
The function of the cooling system is to dissipate part of the heat absorbed by the heated parts in time to ensure that the engine works at the optimum temperature. The cooling system of a water-cooled engine usually consists of a cooling water jacket, a water pump, a fan, a water tank, a thermostat, and the like.
(4) Lubrication system
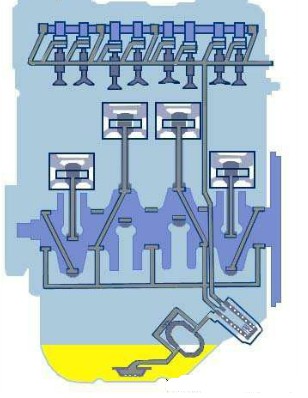
Lubrication system
The function of the lubrication system is to deliver a quantitative amount of clean lubricating oil to the surface of the relatively moving parts to achieve liquid friction, reduce frictional resistance, and reduce wear and tear on the parts. The surface of the part is cleaned and cooled. The lubrication system usually consists of a lubricating oil passage, an oil pump, an oil filter, and some valves.
(5) Ignition system
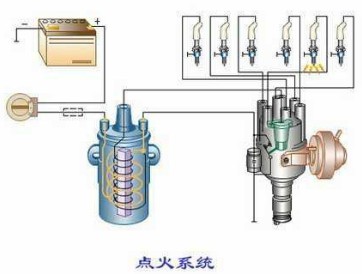
In a gasoline engine, the combustible mixture in the cylinder is ignited by an electric spark. For this purpose, a spark plug is mounted on the cylinder head of the gasoline engine, and the head of the spark plug extends into the combustion chamber. All devices capable of generating an electric spark between the spark plug electrodes on time are called an ignition system, and the ignition system is usually composed of a battery, a generator, a distributor, an ignition coil, and a spark plug.
The difference between gasoline engine and diesel engine construction
The gasoline engine consists of two major mechanisms, namely the crank linkage mechanism, the gas distribution mechanism and the five major systems, namely the fuel supply system, the lubrication system, the cooling system, the ignition system and the starting system;
The diesel engine consists of the above two major mechanisms and four major systems, namely, the crank linkage mechanism, the gas distribution mechanism, the fuel supply system, the lubrication system, the cooling system and the starting system. The diesel engine is compression-ignited and does not require an ignition system.
to sum up
It can be said that the car engine is the origin of car power and an indispensable part of car construction. This paper briefly introduces the two major mechanisms and five major systems of automobile engine construction, and briefly describes the differences between gasoline engine and diesel engine construction.
Single Gang Trailing Socket,Philippines Charger Socket,Philippines Sockets Plugs,Power Outlet Converter Philippines
Heikki Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.heikkipower.com